Observação
Clique aqui para baixar o código de exemplo completo
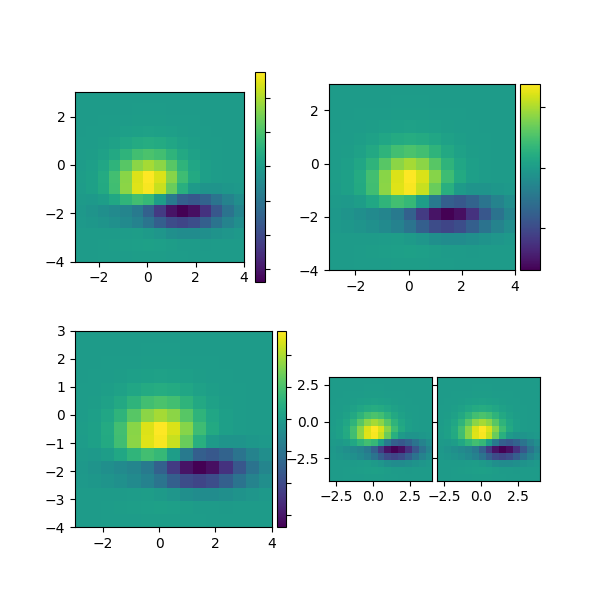
Divisor de eixos #
Divisor de eixos para calcular a localização dos eixos e criar um divisor para eles usando instâncias de eixos existentes.
from matplotlib import cbook
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_demo_image():
z = cbook.get_sample_data("axes_grid/bivariate_normal.npy", np_load=True)
# z is a numpy array of 15x15
return z, (-3, 4, -4, 3)
def demo_simple_image(ax):
Z, extent = get_demo_image()
im = ax.imshow(Z, extent=extent)
cb = plt.colorbar(im)
cb.ax.yaxis.set_tick_params(labelright=False)
def demo_locatable_axes_hard(fig):
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import SubplotDivider, Size
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.mpl_axes import Axes
divider = SubplotDivider(fig, 2, 2, 2, aspect=True)
# axes for image
ax = fig.add_axes(divider.get_position(), axes_class=Axes)
# axes for colorbar
# (the label prevents Axes.add_axes from incorrectly believing that the two
# axes are the same)
ax_cb = fig.add_axes(divider.get_position(), axes_class=Axes, label="cb")
h = [Size.AxesX(ax), # main axes
Size.Fixed(0.05), # padding, 0.1 inch
Size.Fixed(0.2), # colorbar, 0.3 inch
]
v = [Size.AxesY(ax)]
divider.set_horizontal(h)
divider.set_vertical(v)
ax.set_axes_locator(divider.new_locator(nx=0, ny=0))
ax_cb.set_axes_locator(divider.new_locator(nx=2, ny=0))
ax_cb.axis["left"].toggle(all=False)
ax_cb.axis["right"].toggle(ticks=True)
Z, extent = get_demo_image()
im = ax.imshow(Z, extent=extent)
plt.colorbar(im, cax=ax_cb)
ax_cb.yaxis.set_tick_params(labelright=False)
def demo_locatable_axes_easy(ax):
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
ax_cb = divider.append_axes("right", size="5%", pad=0.05)
fig = ax.get_figure()
fig.add_axes(ax_cb)
Z, extent = get_demo_image()
im = ax.imshow(Z, extent=extent)
plt.colorbar(im, cax=ax_cb)
ax_cb.yaxis.tick_right()
ax_cb.yaxis.set_tick_params(labelright=False)
def demo_images_side_by_side(ax):
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
Z, extent = get_demo_image()
ax2 = divider.append_axes("right", size="100%", pad=0.05)
fig1 = ax.get_figure()
fig1.add_axes(ax2)
ax.imshow(Z, extent=extent)
ax2.imshow(Z, extent=extent)
ax2.yaxis.set_tick_params(labelleft=False)
def demo():
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
# PLOT 1
# simple image & colorbar
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1)
demo_simple_image(ax)
# PLOT 2
# image and colorbar whose location is adjusted in the drawing time.
# a hard way
demo_locatable_axes_hard(fig)
# PLOT 3
# image and colorbar whose location is adjusted in the drawing time.
# a easy way
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3)
demo_locatable_axes_easy(ax)
# PLOT 4
# two images side by side with fixed padding.
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 4)
demo_images_side_by_side(ax)
plt.show()
demo()