Observação
Clique aqui para baixar o código de exemplo completo
Demonstração de etiqueta de barra #
Este exemplo mostra como usar a bar_labelfunção auxiliar para criar rótulos de gráfico de barras.
Consulte também os exemplos de gráficos de barras agrupadas , de barras empilhadas e de barras horizontais .
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
Defina os dados
Gráfico de barras empilhadas com barras de erro
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
p1 = ax.bar(ind, menMeans, width, yerr=menStd, label='Men')
p2 = ax.bar(ind, womenMeans, width,
bottom=menMeans, yerr=womenStd, label='Women')
ax.axhline(0, color='grey', linewidth=0.8)
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_xticks(ind, labels=['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5'])
ax.legend()
# Label with label_type 'center' instead of the default 'edge'
ax.bar_label(p1, label_type='center')
ax.bar_label(p2, label_type='center')
ax.bar_label(p2)
plt.show()
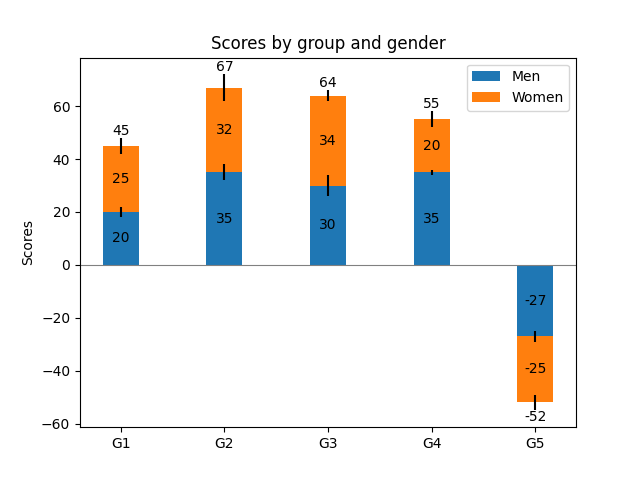
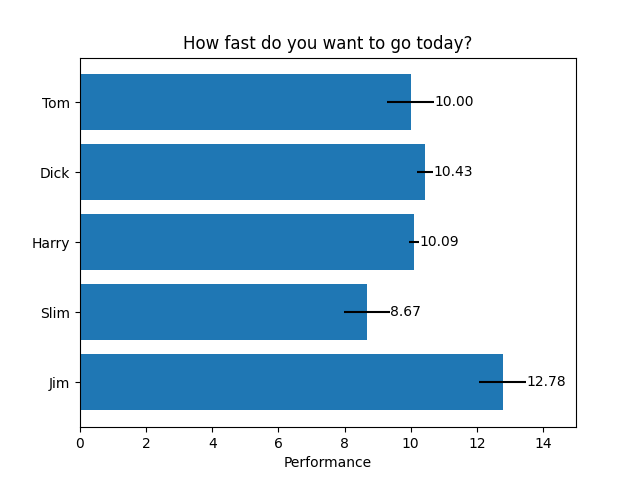
Gráfico de barras horizontais
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
# Example data
people = ('Tom', 'Dick', 'Harry', 'Slim', 'Jim')
y_pos = np.arange(len(people))
performance = 3 + 10 * np.random.rand(len(people))
error = np.random.rand(len(people))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
hbars = ax.barh(y_pos, performance, xerr=error, align='center')
ax.set_yticks(y_pos, labels=people)
ax.invert_yaxis() # labels read top-to-bottom
ax.set_xlabel('Performance')
ax.set_title('How fast do you want to go today?')
# Label with specially formatted floats
ax.bar_label(hbars, fmt='%.2f')
ax.set_xlim(right=15) # adjust xlim to fit labels
plt.show()
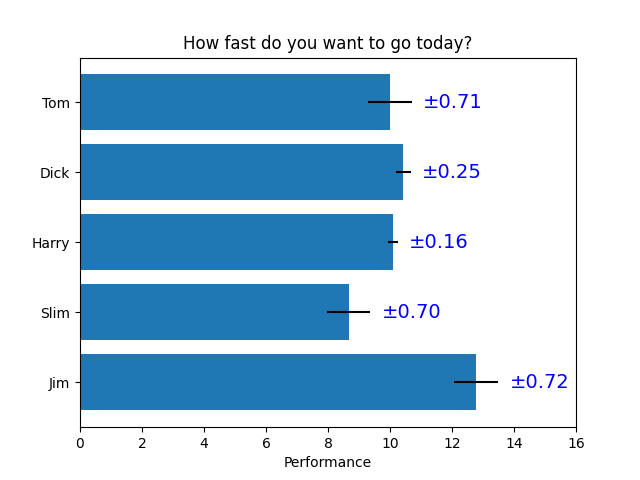
Algumas das coisas mais avançadas que se pode fazer com rótulos de barras
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
hbars = ax.barh(y_pos, performance, xerr=error, align='center')
ax.set_yticks(y_pos, labels=people)
ax.invert_yaxis() # labels read top-to-bottom
ax.set_xlabel('Performance')
ax.set_title('How fast do you want to go today?')
# Label with given captions, custom padding and annotate options
ax.bar_label(hbars, labels=['±%.2f' % e for e in error],
padding=8, color='b', fontsize=14)
ax.set_xlim(right=16)
plt.show()
Referências
O uso das seguintes funções, métodos, classes e módulos é mostrado neste exemplo:
Tempo total de execução do script: ( 0 minutos 1,010 segundos)