Observação
Clique aqui para baixar o código de exemplo completo
Desenhando caixas sofisticadas #
Os exemplos a seguir mostram como plotar caixas com diferentes propriedades visuais.
import inspect
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.transforms as mtransforms
import matplotlib.patches as mpatch
from matplotlib.patches import FancyBboxPatch
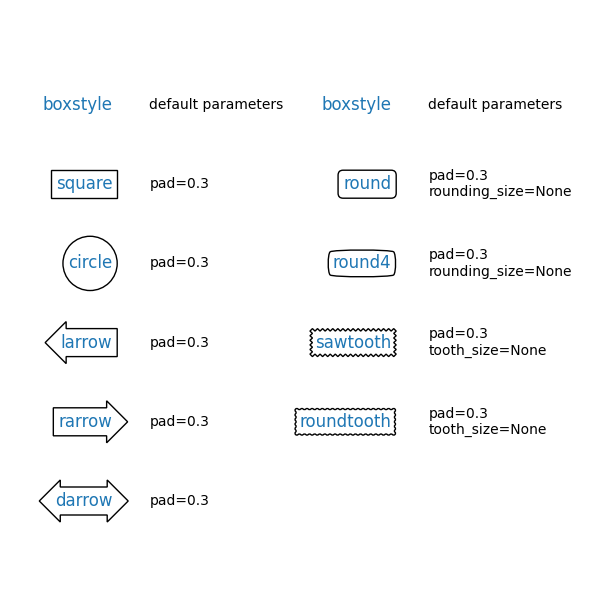
Primeiro, mostraremos algumas caixas de amostra com o fancybox.
styles = mpatch.BoxStyle.get_styles()
ncol = 2
nrow = (len(styles) + 1) // ncol
axs = (plt.figure(figsize=(3 * ncol, 1 + nrow))
.add_gridspec(1 + nrow, ncol, wspace=.5).subplots())
for ax in axs.flat:
ax.set_axis_off()
for ax in axs[0, :]:
ax.text(.2, .5, "boxstyle",
transform=ax.transAxes, size="large", color="tab:blue",
horizontalalignment="right", verticalalignment="center")
ax.text(.4, .5, "default parameters",
transform=ax.transAxes,
horizontalalignment="left", verticalalignment="center")
for ax, (stylename, stylecls) in zip(axs[1:, :].T.flat, styles.items()):
ax.text(.2, .5, stylename, bbox=dict(boxstyle=stylename, fc="w", ec="k"),
transform=ax.transAxes, size="large", color="tab:blue",
horizontalalignment="right", verticalalignment="center")
ax.text(.4, .5, str(inspect.signature(stylecls))[1:-1].replace(", ", "\n"),
transform=ax.transAxes,
horizontalalignment="left", verticalalignment="center")
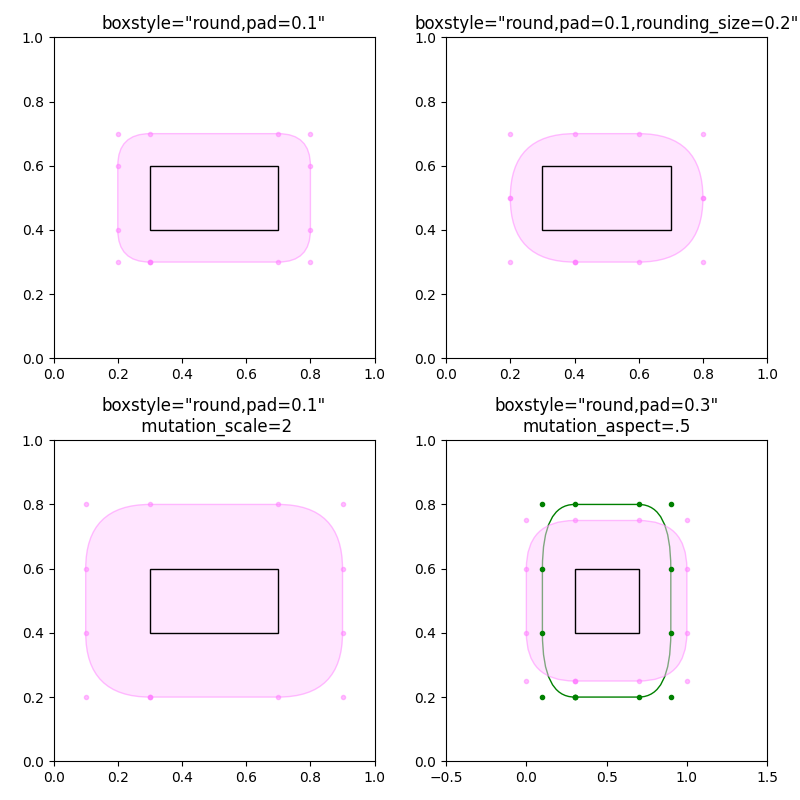
Em seguida, mostraremos várias caixas sofisticadas de uma só vez.
def add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, **kwargs):
fancy = FancyBboxPatch(bb.p0, bb.width, bb.height,
fc=(1, 0.8, 1, 0.5), ec=(1, 0.5, 1, 0.5),
**kwargs)
ax.add_patch(fancy)
return fancy
def draw_control_points_for_patches(ax):
for patch in ax.patches:
patch.axes.plot(*patch.get_path().vertices.T, ".",
c=patch.get_edgecolor())
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 8))
# Bbox object around which the fancy box will be drawn.
bb = mtransforms.Bbox([[0.3, 0.4], [0.7, 0.6]])
ax = axs[0, 0]
# a fancy box with round corners. pad=0.1
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.1")
ax.set(xlim=(0, 1), ylim=(0, 1), aspect=1,
title='boxstyle="round,pad=0.1"')
ax = axs[0, 1]
# bbox=round has two optional arguments: pad and rounding_size.
# They can be set during the initialization.
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.1")
# The boxstyle and its argument can be later modified with set_boxstyle().
# Note that the old attributes are simply forgotten even if the boxstyle name
# is same.
fancy.set_boxstyle("round,pad=0.1,rounding_size=0.2")
# or: fancy.set_boxstyle("round", pad=0.1, rounding_size=0.2)
ax.set(xlim=(0, 1), ylim=(0, 1), aspect=1,
title='boxstyle="round,pad=0.1,rounding_size=0.2"')
ax = axs[1, 0]
# mutation_scale determines the overall scale of the mutation, i.e. both pad
# and rounding_size is scaled according to this value.
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(
ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.1", mutation_scale=2)
ax.set(xlim=(0, 1), ylim=(0, 1), aspect=1,
title='boxstyle="round,pad=0.1"\n mutation_scale=2')
ax = axs[1, 1]
# When the aspect ratio of the axes is not 1, the fancy box may not be what you
# expected (green).
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.2")
fancy.set(facecolor="none", edgecolor="green")
# You can compensate this by setting the mutation_aspect (pink).
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(
ax, bb, boxstyle="round,pad=0.3", mutation_aspect=0.5)
ax.set(xlim=(-.5, 1.5), ylim=(0, 1), aspect=2,
title='boxstyle="round,pad=0.3"\nmutation_aspect=.5')
for ax in axs.flat:
draw_control_points_for_patches(ax)
# Draw the original bbox (using boxstyle=square with pad=0).
fancy = add_fancy_patch_around(ax, bb, boxstyle="square,pad=0")
fancy.set(edgecolor="black", facecolor="none", zorder=10)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Referências
O uso das seguintes funções, métodos, classes e módulos é mostrado neste exemplo:
matplotlib.patches.BoxStyle.get_styles
Tempo total de execução do script: ( 0 minutos 1,556 segundos)