Observação
Clique aqui para baixar o código de exemplo completo
Estilos de caixas personalizadas #
Este exemplo demonstra a implementação de um arquivo BoxStyle. Custom ConnectionStyles e ArrowStyles podem ser definidos de forma semelhante.
from matplotlib.patches import BoxStyle
from matplotlib.path import Path
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Estilos de caixa personalizados podem ser implementados como uma função que recebe argumentos especificando uma caixa retangular e a quantidade de "mutação" e retorna o caminho "mutado". A assinatura específica é a
custom_box_styleabaixo.
Aqui, retornamos um novo caminho que adiciona uma forma de "seta" à esquerda da caixa.
O estilo de caixa personalizada pode ser usado passando
para .bbox=dict(boxstyle=custom_box_style, ...)Axes.text
def custom_box_style(x0, y0, width, height, mutation_size):
"""
Given the location and size of the box, return the path of the box around
it.
Rotation is automatically taken care of.
Parameters
----------
x0, y0, width, height : float
Box location and size.
mutation_size : float
Mutation reference scale, typically the text font size.
"""
# padding
mypad = 0.3
pad = mutation_size * mypad
# width and height with padding added.
width = width + 2 * pad
height = height + 2 * pad
# boundary of the padded box
x0, y0 = x0 - pad, y0 - pad
x1, y1 = x0 + width, y0 + height
# return the new path
return Path([(x0, y0),
(x1, y0), (x1, y1), (x0, y1),
(x0-pad, (y0+y1)/2), (x0, y0),
(x0, y0)],
closed=True)
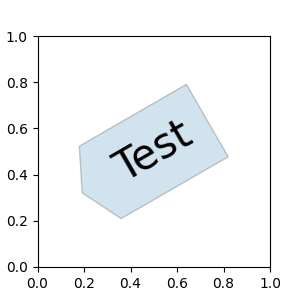
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Test", size=30, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30,
bbox=dict(boxstyle=custom_box_style, alpha=0.2))
Text(0.5, 0.5, 'Test')
Da mesma forma, estilos de caixa personalizados podem ser implementados como classes que implementam
__call__.
As classes podem então ser registradas no BoxStyle._style_listdict, o que permite especificar o estilo da caixa como uma string,
. Observe que esse registro depende de APIs internas e, portanto, não é oficialmente suportado.bbox=dict(boxstyle="registered_name,param=value,...", ...)
class MyStyle:
"""A simple box."""
def __init__(self, pad=0.3):
"""
The arguments must be floats and have default values.
Parameters
----------
pad : float
amount of padding
"""
self.pad = pad
super().__init__()
def __call__(self, x0, y0, width, height, mutation_size):
"""
Given the location and size of the box, return the path of the box
around it.
Rotation is automatically taken care of.
Parameters
----------
x0, y0, width, height : float
Box location and size.
mutation_size : float
Reference scale for the mutation, typically the text font size.
"""
# padding
pad = mutation_size * self.pad
# width and height with padding added
width = width + 2.*pad
height = height + 2.*pad
# boundary of the padded box
x0, y0 = x0 - pad, y0 - pad
x1, y1 = x0 + width, y0 + height
# return the new path
return Path([(x0, y0),
(x1, y0), (x1, y1), (x0, y1),
(x0-pad, (y0+y1)/2.), (x0, y0),
(x0, y0)],
closed=True)
BoxStyle._style_list["angled"] = MyStyle # Register the custom style.
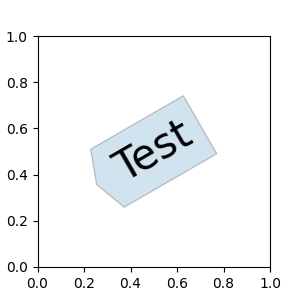
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Test", size=30, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30,
bbox=dict(boxstyle="angled,pad=0.5", alpha=0.2))
del BoxStyle._style_list["angled"] # Unregister it.
plt.show()